Asian elephants are magnificent creatures found in Asia and are the continent’s largest land mammals. Spread over 13 countries, they live in a wide variety of habitats, from grasslands to tropical forests. However, their intelligence and complex social structure enable them to adapt to the available resources in a changing environment. Unfortunately, their once vast domains are shrinking due to a number of human threats. The biggest threat to Asian elephants is habitat loss and fragmentation. Their number has been reduced by about half in the last 60-75 years. Today there are less than 52,000 Asian elephants left in the wild. They are also listed as endangered species on the IUCN Red List.
Why Are Asian Elephants Endangered?
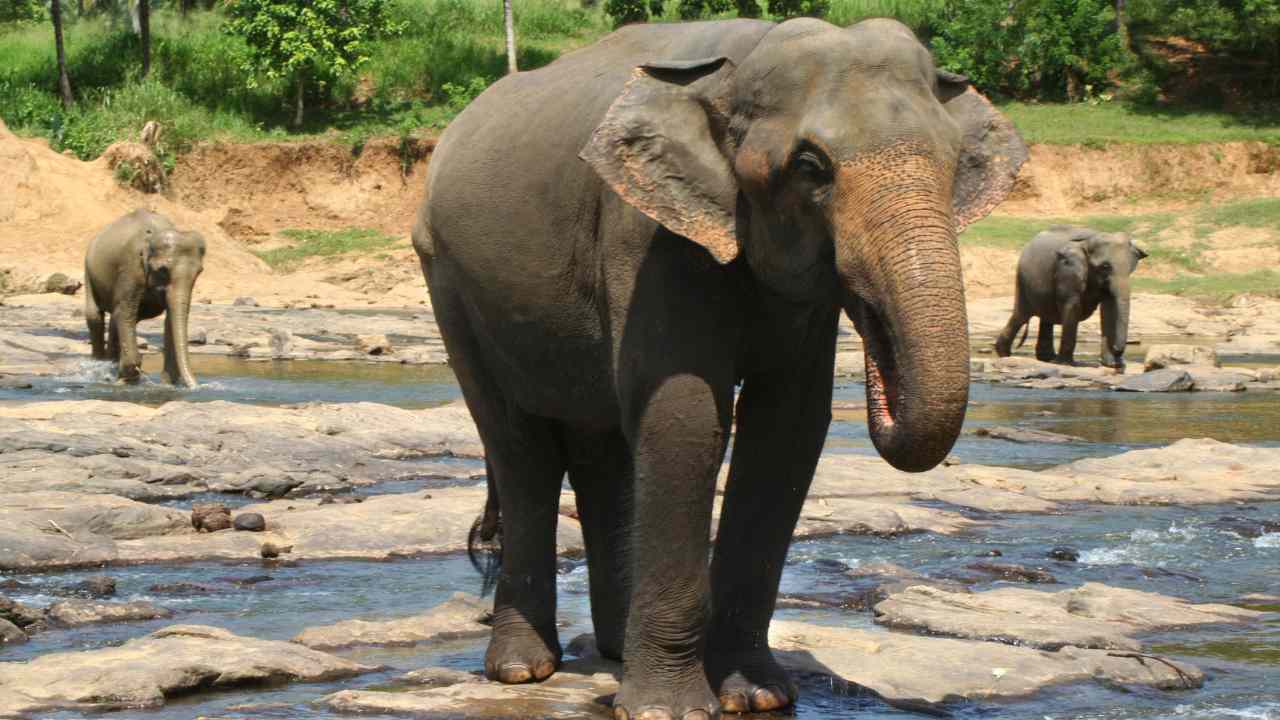

Asian Elephants are the majestic giants of Asia and now are dangerously close to extinction. Their survival is threatened by a range of human-induced factors.
There are several reasons for their endangerment.
- Habitat loss and fragmentation, Asian elephants have lived in these regions for centuries, and their presence is part of the natural ecological history of these areas.
- Diverse Habitats, Asia provides a wide range of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and wetlands, which offer various food sources and shelter for the elephants.
- Ecological Adaptation, Asian elephants have adapted to different environments, enabling them to thrive in these diverse landscapes.
They are losing their homes, facing conflicts with humans, being hunted for their ivory, and having trouble finding mates due to their shrinking populations. Moreover, humans are wiping out the natural habitat of Asian elephants i.e. the forests. This puts them at the risk of becoming extinct.
How many Asian elephants are left in the world?
In 2000, there were more than 100,000 Asian elephants left. But now according to WWF, there are approximately 30,000 to 40,000 individuals left. These numbers vary across different regions and subspecies. The Asian elephant’s status as endangered is primarily due to habitat loss, poaching, and other activities.
Why are Asian elephants important in the ecosystem?
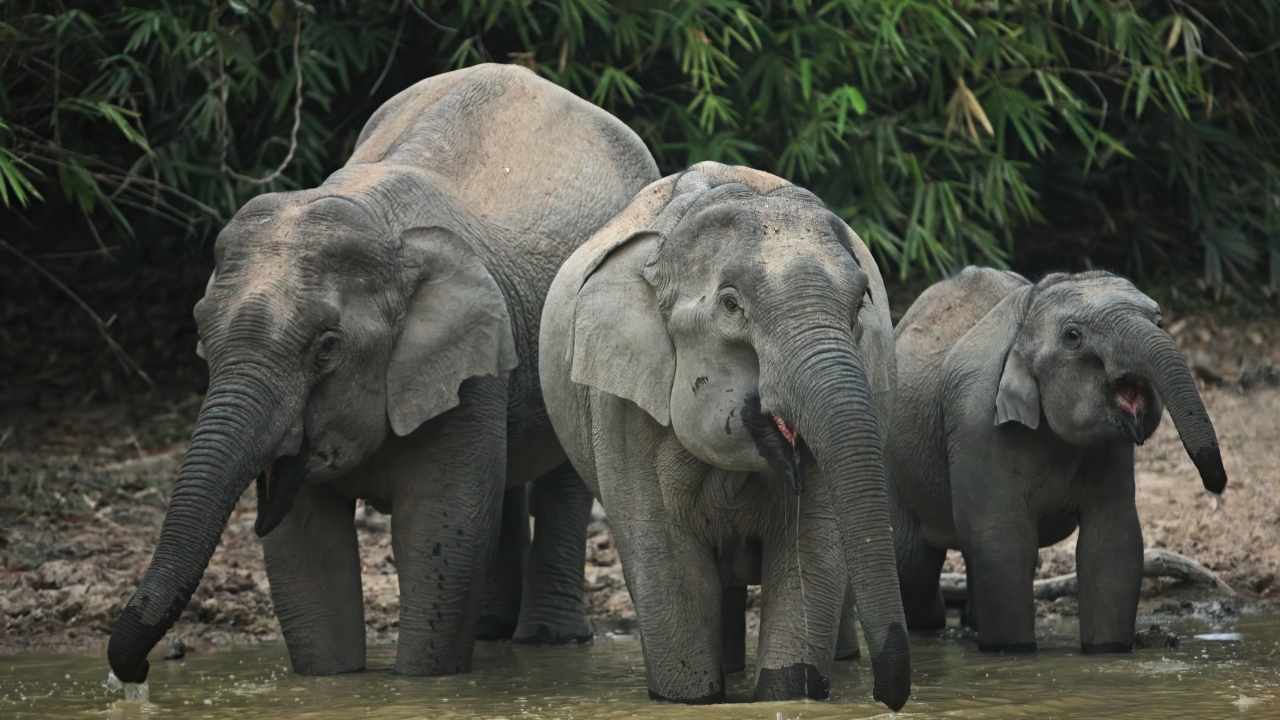

Asian elephants are essential for ecosystem health, cultural significance, and biodiversity. They disperse seeds, create clearings, and provide water sources in their habitats, benefiting various species. Culturally, they hold deep significance and drive tourism. Their presence promotes biodiversity and helps prevent wildfires. Preserving Asian elephants is vital for maintaining balanced ecosystems and protecting cultural heritage.
Where do Asian elephants live?
Asian elephants are found in a variety of habitats across several countries in Asia. They can be found in:
- India
- Sri Lanka
- Nepal
- Bhutan
- Bangladesh
- Thailand
- Myanmar
- Malaysia
- Cambodia
- Vietnam
- Indonesia
Asian elephants are native to a wide range of habitats across Asia. They live in their habitats because these areas historically provide food, water, and shelter. Over time, these elephants have adapted to different environments. However, their homes are disappearing due to deforestation and human activities, which is making it harder for Asian elephants to survive.
When did Asian elephants become endangered?
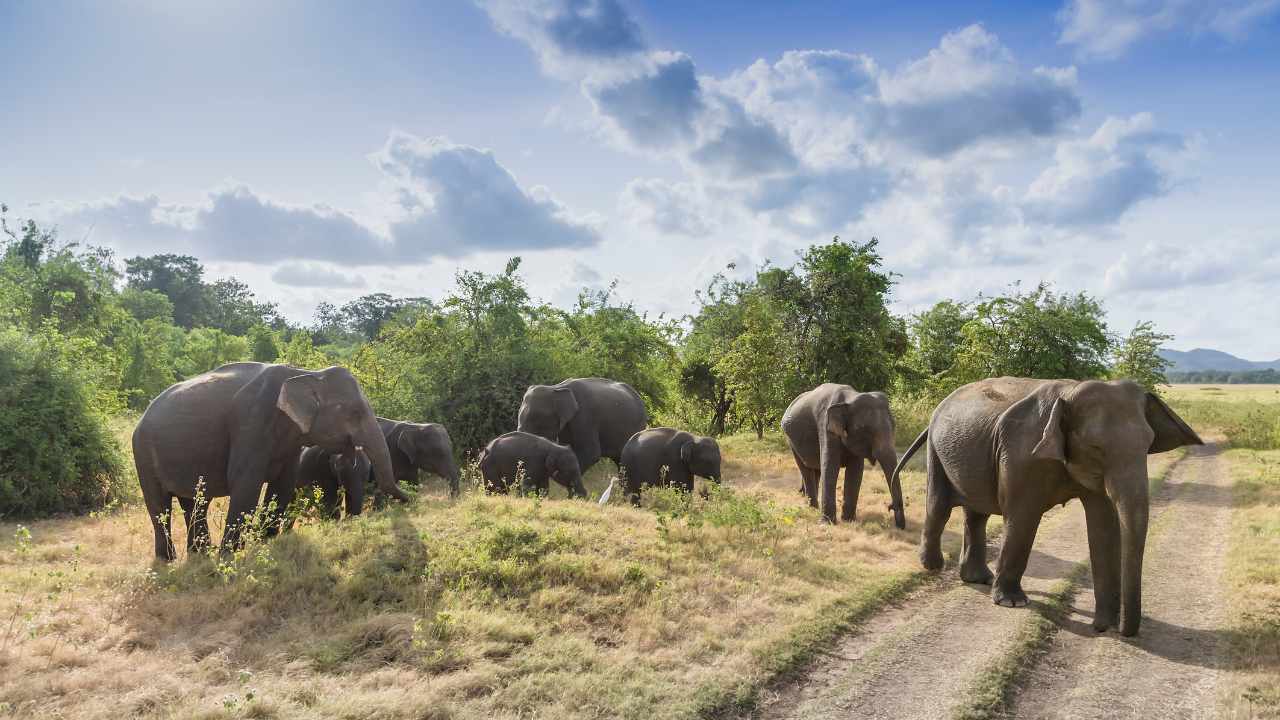

The exact timeline of when they were officially labeled as endangered can be traced back to the establishing of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species in 1986. Asian elephants have been facing a population decline and have been classified as endangered for several decades. (IUCN) indicated that their populations have been declining due to various threats like Habitat loss and poaching.
Why are Asian elephants more endangered than African elephants?
Asian elephants are more endangered than Asian elephants mainly because of habitat loss, human-elephant conflicts, smaller populations, and less international focus on their conservation. Unlike African elephants with large tusks, Asian elephants have smaller tusks, which reduces the incentive for poaching. However, African elephants receive more international attention and resources for conservation due to their larger population and iconic status.
How can we save these Elephants?
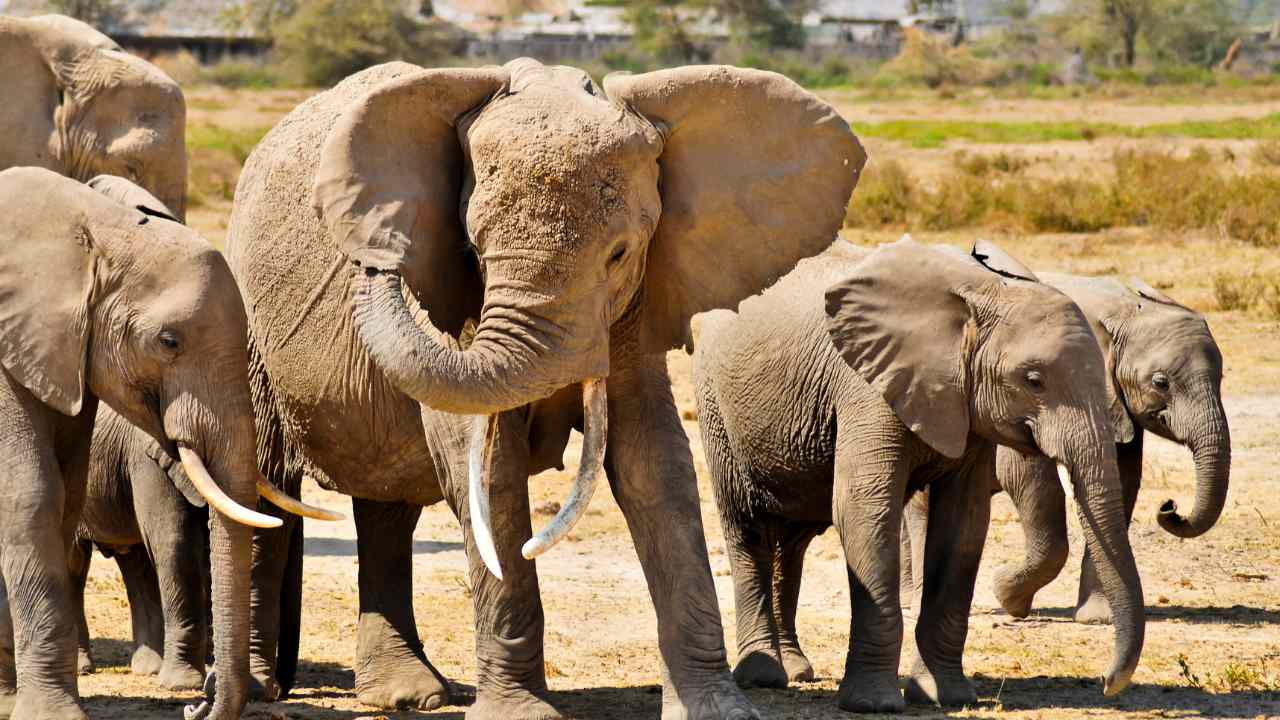

To save Asian elephants, we must protect their habitats, combat poaching, and reduce conflicts with humans. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, regulating ethical tourism, and advocating stricter laws are crucial. Raising awareness and addressing climate change also play vital roles in preserving these iconic creatures and their ecosystems.








